Technical running terms
You're here: Home / Technical terms

Aerobic :
The body, in order to function properly during sports, needs an energy source to supply the muscles. For the runner, as long as it does not reach 85-90% of its Maximum Aerobic Speed, the body uses oxygen to supply the muscles with energy. Aerobic corresponds to this state where the body works only with inspired air. As soon as 85-90% of MAS is exceeded, another energy sector is set up, anaerobic.
Anaerobic :
The body, in order to function properly during sports, needs an energy source to supply the muscles. For the runner, as soon as he exceeds 85-90% of its Maximum Aerobic Speed, the body can no longer be satisfied with only aerobic function and must use the glycogen present in the muscles and the liver to supply the muscles with energy. Beyond about 3 minutes of effort in the anaerobic sector, the breakdown of glycogen into ATP leads to an increase in lactate in the blood. The accumulation of lactate in the blood disrupts muscle effort after 2 to 3 minutes.
ATP :
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the molecule that provides the energy used to contract muscles. One molecule of glucose (sugar) makes it possible to produce two molecules of ATP during glycolysis. Glycolysis does not require oxygen.
Contracture :
Contracture is a painful and unusually long muscle contraction. It's easily differentiated from the cramp which lasts less time. It's better to avoid doing sports in the presence of a contracture to avoid aggravating towards a stretching or a muscle tear.
Core workout :
The core workout strengthens the muscles, especially the deep abs to protect the intervertebral discs and ensure a good tonic effect on the trunk. For running, the core workout allows, at each ground impact, to the body collapses less, which induces a lower risk of injury. This muscle building is really very important for the runner and you will find exercises to do here.
Cramp :
Cramp is a very painful muscle contraction, but one that does not usually last long. It is easily differentiated from contracture which lasts longer. The causes of cramps are still unknown, but it seems that some people are more prone to it than others.
Crossfit :
Crossfit is a new discipline that combines gymnastics, weightlifting, bodybuilding and endurance sports. This sport is an excellent complement to running as a cross training.
Cross training :
Cross training consists in varying sports to avoid that the same joints or the same muscle groups are always solicited in the same way. The goal is to avoid injuries. To alternate with running, do cycle, swim or crossfit.
DNF :
The abbreviation DNF (Did Not Finish) is often found on race results. This means that the participant has not finished the race, which corresponds to a withdrawal.
DNS :
The abbreviation DNS (Did Not Start) is often found on race results. This means that the participant did not start the race.
Drop :
The drop is the difference in sole height between the front of the foot and the rear. In common shoes, the drop is generally 12mm, which means that the sole at the back of the foot is 12mm thicker than the front. In minimalist shoes the drop is generally low (<4mm).
Ekiden :
The Ekiden is a relay race that originated in Japan. The distance to be covered is equal to the marathon, 42.195 km. There are 6 torchbearers who must cover 5km, 10km, 5km, 10km, 5km and 7,195km. You can find races called ekiden with a different number of runners.
Endurance :
Endurance is the ability to maintain an effort, with a certain degree of intensity, for a certain duration. Endurance is unique to everyone, it can be improved through training and is important for performance on races starting from the distance of half-marathon just like the MAS.
Fartlek :
Fartlek (which means "speed game" in Swedish) is an interval training method like interval workout. The principle is to vary its pace for durations which can also be variable without taking into account the terrain which can be hilly. Learn more on the dedicated article.
GPP :
Diminutive of General Physical Preparation, this workout is very important for the runner. This muscle preparation is specifically studied to strengthen the muscles used during running. You will find exercises to do here.
Half-Marathon :
The half-marathon is a running race which takes place over a distance of half a marathon, or 21.1km. The fastest run the distance in less than an hour.
Heart rate monitor :
It's a portable device that allows you to measure your heartbeat. There are different kinds but are now integrated in almost all sports / GPS watches, some take the measurement directly on the wrist but are a little less precise than those taking the measurement with a chest strap. Most allow to record the cardiac variations during the effort and give an analysis of the data on computer.
HR max :
It's the maximum heart rate (number of heart beats per minute). It's unique to everyone and the older we get, the more it decreases. It can be measured during a stress test with the help of an heart rate monitor.
Hypoglycemia reaction :
About 30 minutes after ingesting sugars, your pancreas will secrete insulin to lower your blood sugar. If you add sport at this time, insulin doing its action of storing sugar in adipose tissue will not make sugar available for the muscles, it is hypoglycemia reaction.
INSEP:
The French National Institute of Sport, Expertise and Performance is a center of excellence for high-level athletes located in Paris, in the Bois de Vincennes.
It has specific sports equipment, medical and recovery infrastructure, accommodation and also offers athletes personalized support in terms of training.
Interval workout :
Interval workout is a training method that alternates fast-paced work followed by a recovery period, active or passive. This method, with the rest phases, allows you to work longer at a steady pace compared to a sustained pace session done without the rest phases, for the same gain. Learn more about on the dedicated article.
Ironman :
Very demanding triathlon event, the distances to be covered are 4 km in swimming, 180km by bicycle and a marathon (42,195km) to finish. The most famous events in France are the Ironman of Nice and the Embrunman. If you want to participate to this kind of trial, discover how to prepare yourself in less than one year.
Ischemia :
It is a phenomenon linked to sports activity, mainly endurance sports. With the effort, the blood leaves the viscera to feed the muscles which disturbs digestion.
Lactate :
Lactic acid (or lactate) is a "waste" of energy production in the muscles. In anaerobic (oxygen deficiency), lactates are produced in quantity and accumulates in the blood. According to the latest research, lactate is not responsible for body Stiffness. It has also recently become known that lactate can be recycled for energy. Some workouts, such as the lactate shuttle, allow the body to better recycle lactates.
LT1 :
The LT1 pace corresponds to the pace at which the body begins to no longer be able to transform all the lactate produced. This pace is approximately 78% of the MAS (Maximum Aerobic Speed) or about 80% of the HR max. It’s slightly faster than the marathon pace.
LT2 :
The LT2 pace corresponds to the pace at which the difference between the lactate produced and the processed lactate increases significantly. This pace is approximately 85% of the MAS, or approximately 90% of the HR max. It’s this pace that we usually talk about when we talk about threshold training.
M1 / M2 / M3 / M4 :
The Athletics Federation has established several categories according to age: hopes, seniors, masters. Category M1 corresponds to the group aged 40-49 years, M2 to 50-59 years, M3 to 60-69 years, M4 to 70-79 years .
Marathon :
The marathon is a running race present at the Olympic games. For the past few years, the record for this 42.195km event has been steadily improving to approach the 2 hour mark. The origin of this race goes back to the battle of Marathon in 490 where the Greek messenger Philippidès would have run from Marathon to Athens to announce the victory against the Persians, arrived breathless he would have died after having delivered his message.
MAS :
MAS, short for Maximum Aerobic Speed, is the speed at which we reach our maximum oxygen consumption.
This is a speed that the runner is able to hold for about 6 minutes.
It's possible to run beyond this speed for shorter times but the body must appeal to the anaerobic (without oxygen).
Learn more about on the dedicated article.
Mesh :
The “mesh” corresponds to the fabric on the top of the running shoe. It can be more or less tight depending on the shoes and determines the ventilation and humidity in rainy weather that the shoe will let through. It will be tighter for trail shoes, more ventilated for road shoes.
Minimalism :
Minimalism consists in running with little cushioning shoes or downright bare feet, this going against modern society which favors cushioning to avoid injury. It's a fairly recent movement which was highlighted by the book "Born to run" by Christopher McDougall with the Mexican tribe of tarahumaras who run very long distances with simple sandals.
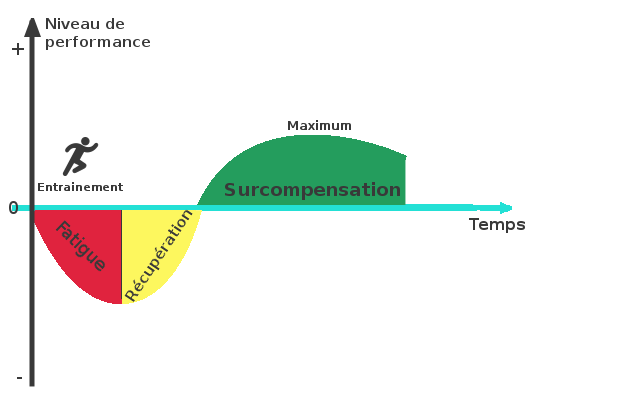
Overcompensation :
During a training session that demands enough to the body, it gets tired, and if the recovery after this training is dosed enough, the body adapts to reach a level higher than before training, it's overcompensation.
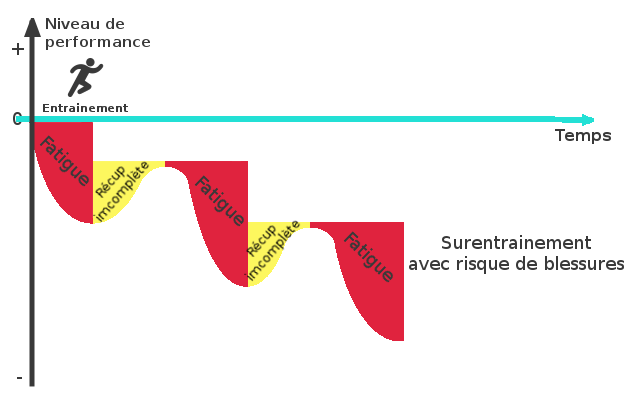
Overtraining :
During a training session that demands enough to the body, it gets tired, if the recovery after this training is not enough, fatigue sets in and accumulates with the following training sessions, this is overtraining.
Sleep can be disturbed, you feel tired, less motivated and the risk of injury increases.
Oxidative stress:
Oxidative stress involves molecules, called free radicals, that permanently attack the body and cause cells damages. The only way to actively fight is to consume enough antioxidant (especially present in fruits and vegetables) to fight the free radicals generated by sports activity.
Pacemaker (sometimes called a rabbit) :
Fast runner who quickly leads the peloton in the first laps of the track and then completely relax their effort to finish far behind, when they don't just give up.
Plyometrics :
Plyometrics is a training aimed at making the muscles work in explosiveness and in power. The principle is to do a quick stretch of a muscle group followed by its contraction. During this work, the proprioceptive receptors of the muscles are activated.
An easy exercise is to get high (30 to 40 cm), jump below and as soon as the feet touch the ground, try to jump vertically as high as possible.
Pronation :
The stride is said to be pronator when the outer edge of the foot first touches the ground and then pours inward. The wear of the shoe is marked on the outer edge of foot's rear and on the inner edge of the forefoot.
Proprioception :
Proprioception is the perception, conscious or not, on the positionning of body different parts. It works thanks to numerous muscle and ligament receptors. Learn more about on the dedicated article.
Reperfusion :
It's a phenomenon linked to sports activity, mainly endurance sports. After the effort, the blood returns to the viscera suddenly which damages the intestines and disturbs digestion.
SP10 :
This acronym stands for 10km Specific Pace, in other words, it's the pace that you are able to maintain during a 10km race. In the 10km preparation training plans, this acronym will correspond to the pace you are aiming for your competition.
SP21 :
This acronym stands for half marathon Specific Pace, in other words, it's the pace that you are able to maintain during a half-marathon. In half-marathon preparation training plans, this acronym will correspond to the pace you are aiming for your competition.
SP42 :
This acronym stands for marathon Specific Pace, in other words, it's the pace that you are able to maintain during a marathon. In marathon preparation training plans, this acronym will correspond to the pace you are aiming for your competition.
Stiffness :
Stiffness are muscle pain that usually appears between 24 and 48 hours after an unusual effort. It's now accepted that lactates are not responsible for that. The real culprit seems to be the micro-traumas and the benign muscular lesions which are done during a greater effort than usual (like the Interval training, a long run or an run with a lot of elevation.
Stretching :
Stretching the muscle allows it to return to its original length and helps maintain good range of motion. Learn more about on the dedicated article.
Supination :
The stride is said to be supinator when the outer edge of the foot first touches the ground and then it remains on the outer edge. The wear of the shoe is marked on the outer edge of foot's rear and on forefoot.
Swimrun :
Relatively recent sports event from Sweden, which consists of running and swimming in a natural environment. Unlike aquathlon, there are several swimming portions and several running portions. This race is generally run by teams of 2 people.
Toebox :
Indicates the front part of the shoe, the place where the toes are arranged. Some shoe brands such as the ALTRA brand have chosen to make a forefoot that more closely matches the natural foot shape with a wider forefoot.
Trail :
Sports running race which generally takes place in a natural environment. The big difference with road racing lies in the fact that there is often an elevation that forces runners to change their pace or even walk on the steepest hills.
In recent years, urban trails have also appeared, where stairs replace natural elevation. Fartlek training is particularly suitable to progress on trail.
Triathlon :
Sports discipline consisting of doing three different sports one after the other, swimming, cycling and running. Several distances exist allowing beginners as well as experienced to participate.
Ultra-trail :
The ultra-trail is a running race which takes place in natural environment with elevation and whose total distance is more than a marathon (so more than 42 km). There are famous ultra-trail with distance of more than 160km like the UTMB (which goes around Mont-Blanc mountain) or the diagonale des fous (running event on the island of Reunion).
Vo2 max :
By analogy with a car, Vo2 max corresponds to the engine size of your body. It's the maximum oxygen consumption in liters per minute but it's easier to express it in ml of O² per kilogram of body weight and per minute (ml O²/kg/min).


