

Importance in performance
According to a definition from the INSEP; The dietary balance of the sportsperson allows to better support training sessions to get better, not to switch into overwork / overtraining, to avoid the risks of injuries, to better recover after training sessions and competitions and stabilizes its weight, all of which contribute to a progression in performance throughout the season.
In recent years, our diet has been increasingly poor in nutrients. As the table below shows, because of production methods, food provides us with less and less nutrients.
Some examples of micronutrients usefulness :
- - Selenium is important because it's active in 300 interactions in the body.
- - Magnesium is used for muscle contraction and neurons.
| From 1950 to the present day | |
|---|---|
| Apple | 100 times less vitamin C. |
| Potato | 45% less iron and 35% less calcium. |
| Broccoli | 80% less copper. |
| Orange | 21 times less vitamin A. |
To overcome this problem, you can eat organic food, which contains about 40% more nutrients, compared to food produced with pesticides.
Besides, today, the sportsman's diet is too rich in energy and too poor in micronutrients.
So that micronutrients are better assimilated, remember to chew well before swallowing.
Sportsman, an individual apart
The training causes changes in the body that must be taken into consideration :
| Before the effort | After the effort | |
|---|---|---|
| Water status | Normal | Decreased |
| Digestive circulation | Normal | Lowered |
| Immunity | Normal | Lowered |
| Protein balance | Normal | Negative |
| Glycogen | Saturated | Out of stock |
| Acid / base balance | Slightly alkaline | + or - acid |
| Cell integrity | Preserved | Radical attacks |
Sport causes changes in the body functioning and mainly :
- - An increase in nutrient and micronutrient needs.
- - An increase in "oxidative stress".
- - An acidity increase.
- - Digestive fragility.
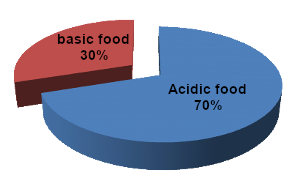
Acidity :
The body works in a slightly alkaline PH environment (around 7.4).
The food we consume is broken down into small molecules by digestion and these have an accidifying or basifying action on the body.
By consuming too many addictive foods, an acidic environment settles in addition to the acidity produced by sport.
To counter this acidity, which can be the cause of injuries, the body consumes its reserves of vitamins and minerals to restore a favorable environment.
You have to be careful, because in extreme cases, the body can get the nutrients it lacks directly from the bones, which can eventually lead to osteoporosis or fatigue fractures.
Accidifying foods to consume moderately are :
- - Animal proteins, especially meat.
- - Dairy products.
- - The cereals.
- - Fruits.
- - Vegetables.
To learn more about acidifying or basifying foods, you can look at the PRAL (Potential Renal Acid Load) index on the internet.
If the PRAL is greater than zero, the food is considered to be acidifying, if it's negative, the food is considered to be alkalizing and the value "zero" signifying neutrality.
Fatty acids :
Our current diet provides on average too much omega 6 compared to omega 3 (40 to 1 ratio). We have to get closer to the harmonious omega 6 / omega 3 ratio of 4 to 1.
Omega 6s are pro-inflammatory while Omega 3s are rather anti-inflammatory.
Here is a summary of the different edible oils available and their omega 6 / omega 3 ratio.
| Types of oil | Omega 6 / Omega 3 ratio |
|---|---|
| Sunflower | 124 |
| Corn | 59 |
| Grape seeds | 43 |
| Peanut | 42 |
| Isio 4 | 39 |
| Soy | 8 |
| Nuts | 5.2 |
| Primrose | 4.5 |
| Rapeseed | 2.4 |
We can see that the best oil to improve the ratio is rapeseed oil, which also has the advantage of being cheap.
- Do not cook rapeseed oil which becomes harmful if it's heated.
Choose an organic oil and drink about 2 tablespoons a day.
Oxidative stress :
Sport, with increasing oxygen consumption during training, is a major supplier of free radicals. The molecules called free radicals attack the body permanently and cause cell damage.
Oxidative stress is caused by the imbalance between the free radicals attack and the body defense capabilities, which are very largely dependent on micronutrient status.
If oxidative stress becomes too important, it can cause injury.
To adequately combat oxidative stress, you need to supply the body with enough antioxidant elements.
A rich and varied diet of organic fruits and vegetables generally meets the needs of athletes, but it's possible to supplement the intake with antioxidant supplements for those who do a lot of sport (more than 10 hours per week).
I also advise you to take spirulina tablets after each hard workout (interval training, long run). Recovery is much better with the help of spirulina which reduces the general fatigue linked to the training.
The case of endurance sports
Phenomenon "Ischemia - Reperfusion"This phenomenon, mainly linked to endurance sports activity, leads during exertion, of a movement of blood from the viscera to the muscles to supply them.
After the effort, the blood returns to the viscera suddenly and attacks the intestinal mucosa.
By dint of repetition, this aggression leads to digestive disorders on exertion and often at rest.
To combat this phenomenon, you should drink regularly from the beginning and until the end of the effort, a drink composed of :
- - Carbohydrates as maltodextrine.
- - Glutamine.
- - Amino acids type BCAA.
- - Alkalizing minerals.
Basic food
The daily plate for better energy should consist of :- - Balanced proteins, 50% from animal sources and 50% from vegetable sources.
- - A mix of rapeseed oil (80%) and olive oil(20%).
- - Vegetables and fruits in quantities.
- - Oilseeds (nuts, almonds, hazelnuts, ...).
- - Sources of starchy foods (wholemeal bread, whole grains, semolina, pasta, ...).
- - 2-3 squares of dark chocolate (70% minimum).
- - Waters with lots of bicarbonates in it.
However, avoid :
- - Caffeinated drinks (which create a leak of magnesium).
- - Cookies and sweets (too much sugar).
- - Cakes and pastries (too much sugar and fat).
- - Sweet drinks (too much sugar).



